Biofuel is a fuel that comes from organic matter, such as plants or animals. The best thing about biofuel is that it is carbon neutral since the CO2 has already been extracted during the organism’s life cycle. That means it doesn’t produce any additional CO2 when burning.
Let’s take a tree as an example. Trees need CO2 to produce oxygen through photosynthesis. They simply absorb CO2 that is already in the atmosphere. When the tree is burnt, CO2 is released back into the environment in exchange for oxygen which fuels the fire. Due to this process, there has been no net-gain in atmospheric CO2.
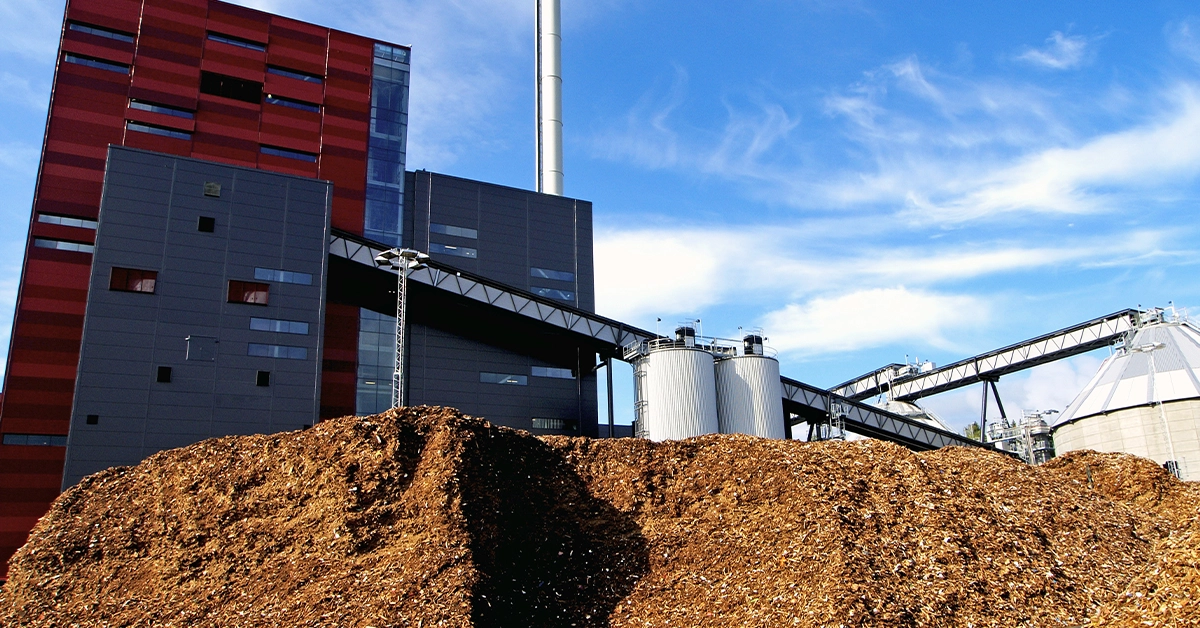
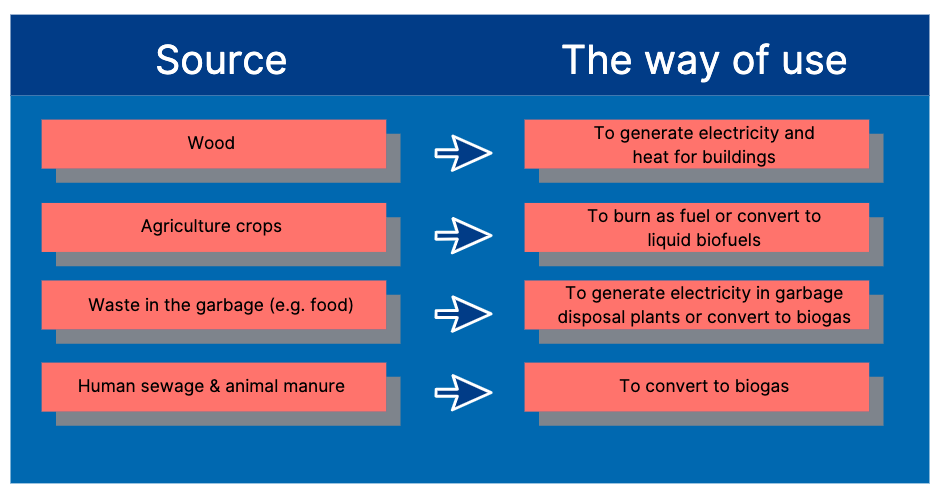
Biomass, as well as biogas, are renewable sources of energy. They are both carbon neutral biofuels, just in different forms. Biomass can be anything from agricultural crops to wood, animal residues, sewage or other industry byproducts that serve no other purpose and would otherwise be dumped in landfills and openly burned.
There are several ways of getting this 100% natural energy biomass. When forestry companies cut trees, not every part of the tree is being used in the process. Branches, rotten wood or leaves are considered a waste product. The leftovers are crushed and are transferred to biomass power plant. The other way how to get biomass is to grow it specifically for that purpose. An example is rapeseed, corn or sugarcane.
How to Use Biomass to Produce Energy
Biomass power plants burn the biomass to convert water to steam. With this steam, heat for buildings or electricity is produced. Biomass can be burned directly or can be converted to a gas called biogas. It can also be converted into biofuels (ethanol or biodiesel) and then be burned for energy. Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils (e.g. rapeseed oil) and animal fats and is usually used in vehicles.
Other ways of using biomass for energy:
A very popular form of biofuel made by the compressed organic matter are pellets. Their small size allows them to be transferred over a long distance. When used for independent heating of the household, they can automatically be fed to the burner. Their high density and low moisture content allow them to burn very effectively.

3 Benefits of Using Biomass as Your New Fuel
Thanks to natural materials, the energy produced out of biomass offer many environmental benefits.
- Biomass annually reduces greenhouse gasses by over 30 million tons of CO2. This is being done only by replacing fossil fuels and preventing the release of greenhouse gases from organic waste.
- Using biomass as a fuel eliminates the need for frequent open burns of agricultural waste which improves the air quality as well.
- Being able to produce energy 24/7 due to the low dependency on weather conditions (unlike the solar panels or windmills) makes it a reliable source of energy.
Biogas: Why to Switch to Biogas from Natural Gas
Biogas is derived from the same organic matter as biomass. With the difference that biogas is the result of fermentation. It is produced during anaerobic micro bacterial degradation processes of organic substances. This multi-stage process, also known as anaerobic digestion, takes place in special containers called “digesters”. There is a natural lack of oxygen which creates gas as the result.
The produced gases are CO2 (35%) and a larger amount of even more damaging greenhouse gas, methane (65%). The facility doesn’t allow methane to escape into the atmosphere because it keeps it in the digester until it is burned to produce energy. After simple processing, biogas is a perfect renewable substitute for natural gas. The digested materials are later used for compost or peat moss.
Bioenergy popularity in the EU and the U.S.
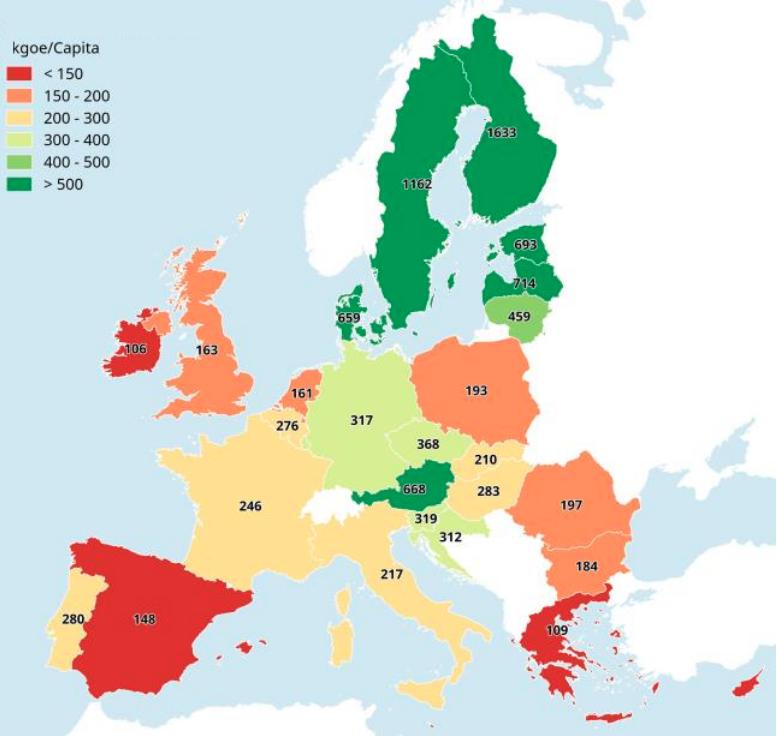
The energy from biomass (bioenergy) plays a key role in achieving the EU's renewable energy target for 2030 and beyond. So far it has been the main source of renewable energy in the EU with a share of 60%. The biggest EU bioenergy consumers per capita are Austria, Scandinavian and Baltic countries.
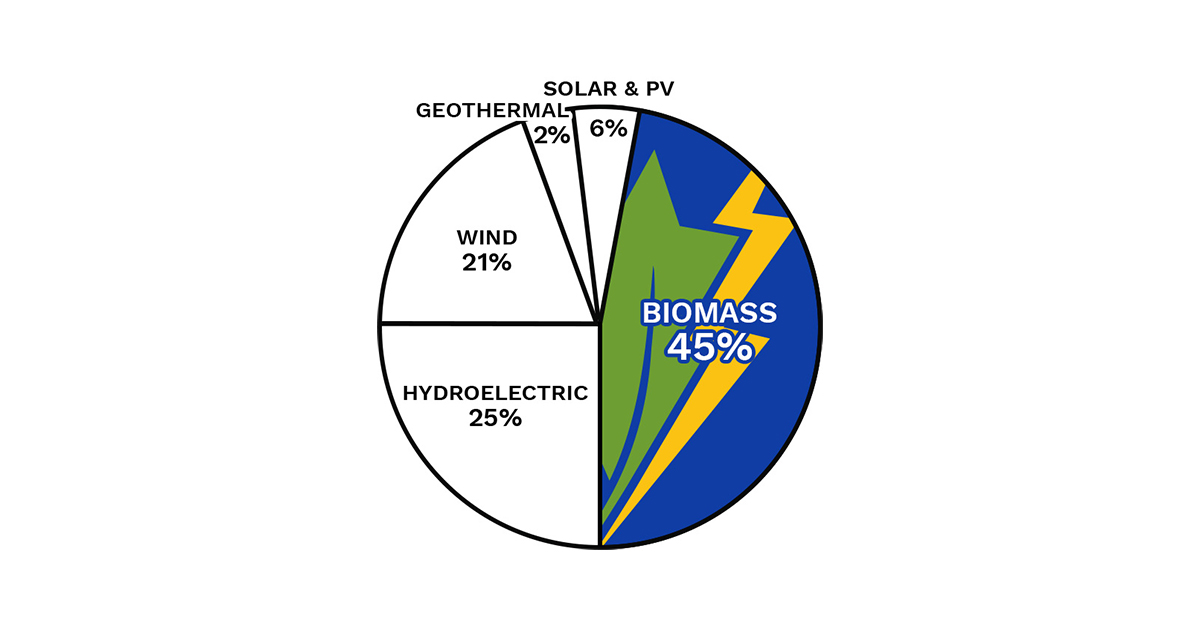
In the U.S. biomass power supplies around half of America’s renewable electricity, which represents about 5% of total primary energy use.
In a modern household, you don’t necessarily need to heat up the rooms with wood leftovers anymore. Imagine pairing your energy source with software that manages your energy consumption in order to reduce your energy costs. FUERGY brings you the opportunity to start producing energy efficiently and shorten the payback period of your investment to 3 years. Comparing to traditional solar panel installation with a payback period of 15-20 years you can count with considerable savings.
Are you ready to be part of the renewable energy revolution and take your energy independence to the next level? Contact us today! Our experts are here to help you find a tailor-made solution to your needs.
New dimension of energy optimization